-
Original Research Article
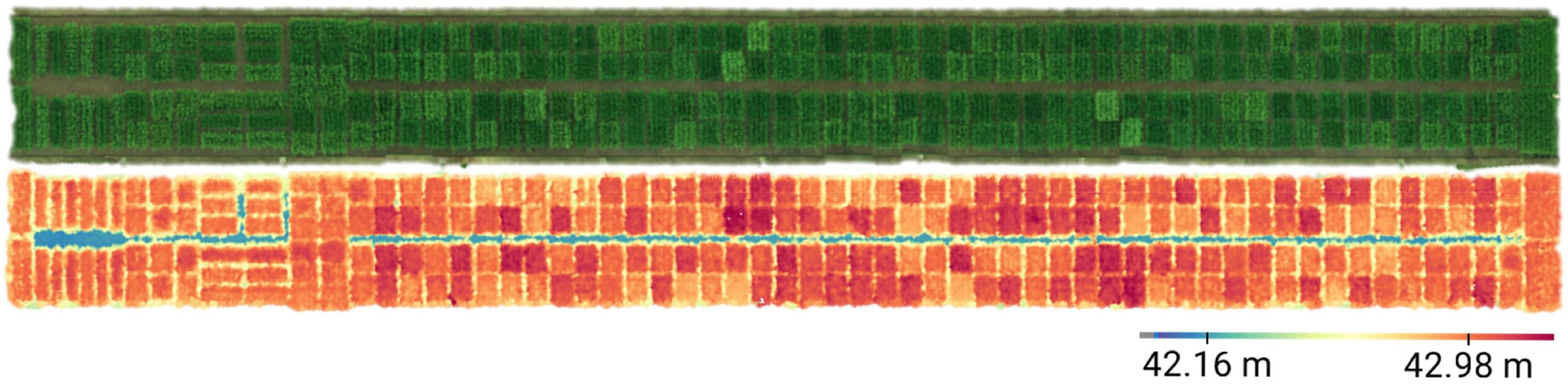
-
Study on the Comparison of Rice Growth Rates Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Imagery and Their Correlation with Yield
드론 영상 기반 벼 계통별 생육속도 비교 및 생산량과의 상관관계 연구
-
Yunjeong Jeong, Ji-hyeong Lee, Do-hyun Kim, Jeonghwan Seo, Sungyul Chang
정윤정, 이지현, 김도현, 서정환, 장성율
- Rice is a staple food for approximately half of the global population and accounts for about 46% of total cultivated land in …
- Rice is a staple food for approximately half of the global population and accounts for about 46% of total cultivated land in South Korea. In recent years, climate change and rural aging have increasingly limited labor-based crop management, driving demand for scientific and efficient crop monitoring technologies. In this study, we utilized Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-based Digital Surface Models (DSM) to calculate the absolute growth rate (AGR) of rice and classified 70 accessions into two groups based on AGR differences before and after the reproductive stage. We then analyzed the relationship between growth characteristics and yield components between the groups. The results showed that Group B, which exhibited continued growth in the late reproductive stage, had significantly higher AGR and yield than Group A. AGR during the reproductive stage was significantly and positively correlated with yield and grains per panicle. Most previous studies have either compared manually measured growth traits with yield, estimated vegetation indices using UAVs, or focused on plant height at a single time point. Thus, studies analyzing time-series growth rates or linking growth patterns with yield components remain limited. In particular, few studies have quantitatively compared productivity by grouping accessions based on growth responses across phenological stages. This study demonstrates the potential of UAV-derived DSMs as a tool for time-series growth monitoring and productivity assessment in rice. Although conducted in a single region with 70 accessions, this approach has strong potential for broader application across diverse environments and genetic resources. - COLLAPSE
-
Study on the Comparison of Rice Growth Rates Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Imagery and Their Correlation with Yield
-
Original Research Article
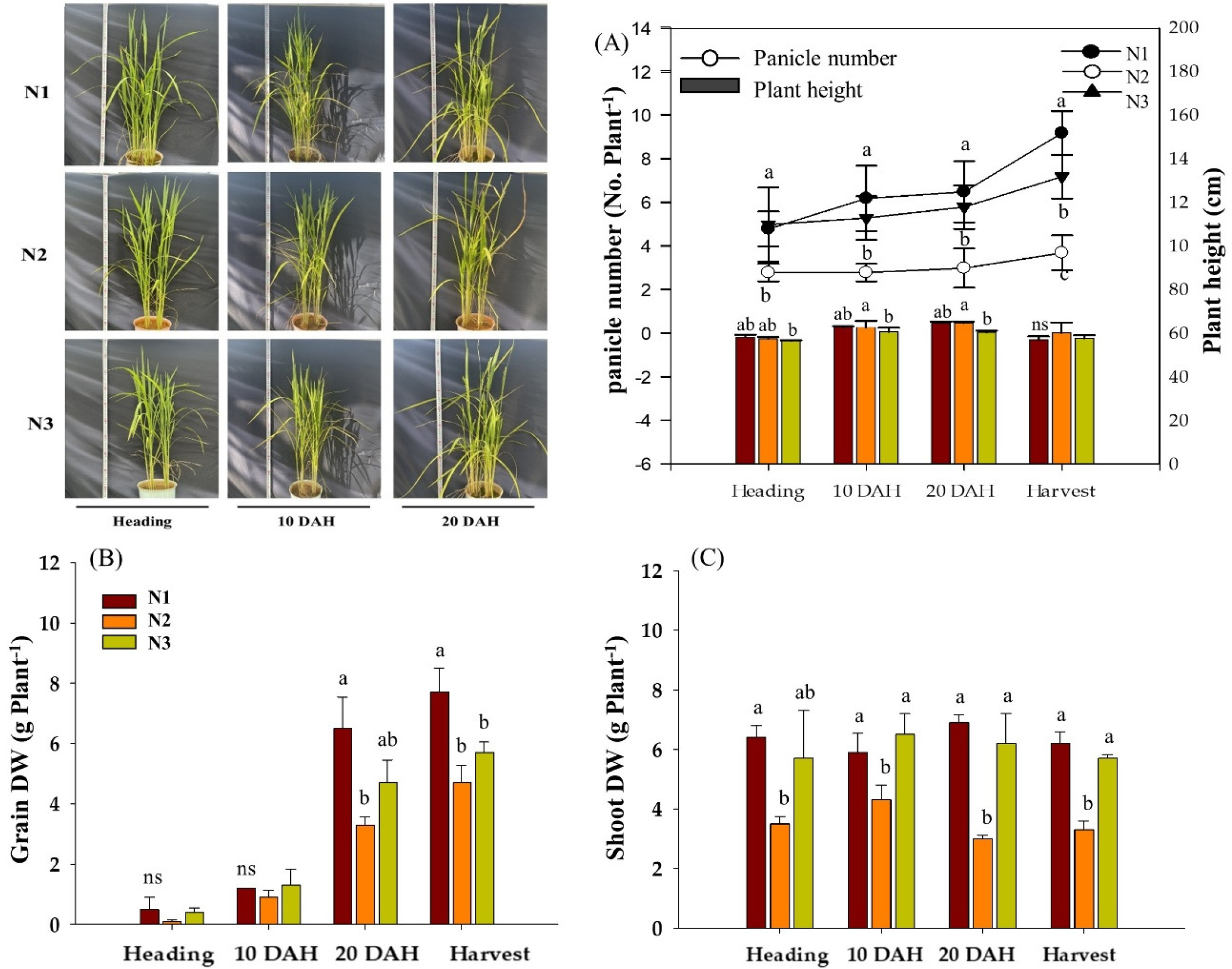
- Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Carbohydrate Metabolism in Rice by Reduced Nitrogen Fertilizations
- Yuna Chang, Jwakyung Sung
- Efficient nitrogen (N) management is critical for enhancing rice (Oryza sativa L.) productivity, while mitigating its environmental impacts. This study evaluated …
- Efficient nitrogen (N) management is critical for enhancing rice (Oryza sativa L.) productivity, while mitigating its environmental impacts. This study evaluated the effects of three N application practices—conventional split (N1: 50–30–20 %), top-dressing only (N2: 0–30–20 %), and basal only (N3: 50–0–0 %)—on growth, nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), carbohydrate metabolism, and sugar transporter gene expression in rice (cv. Ungwang). N2 significantly reduced tillering and biomass; however, it exhibited the highest nitrogen harvest index (NHI), indicating enhanced N remobilization to grains. N3 improved NUE by 46 % and promoted higher soluble sugar and starch accumulation in both shoots and grains. Reduced N inputs (N2 and N3) upregulated the sucrose transporter genes OsSWEET11 and OsSUT1 at later grain–filling stages, supporting stronger source–sink dynamics. Principal component analysis linked N3 with nitrogen utilization efficiency (NUtE) and grain starch accumulation and N2 with NHI and grain soluble sugars. These findings highlight that adjusting N2 and N3 practices can optimize NUE and carbohydrate allocation, offering a sustainable approach for rice production. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Research Article
-
Comparison of Deep Learning and Vegetation Index Methodologies for Estimating Rice Canopy Coverage Based on RGB Images
RGB 영상 기반 시계열 벼 군락 피복도 추정을 위한 딥러닝 모델과 식생지수 방법론 비교
-
Eun-Ji Kim, Do-Hyun Kim, In-Ha Lee, Sungyul Chang, Dongwon Kwon, Woo-jin Im, Woon-Ha Hwang, Wan-Gyu Sang, Jae-Ki Chang, Hyeok-jin Bak
김은지, 김도현, 이인하, 장성율, 권동원, 임우진, 황운하, 상완규, 장재기, 박혁진
- Canopy coverage is a key agronomic trait for assessing rice growth and predicting grain yield. However, conventional measurement methods are labor-intensive and …
- Canopy coverage is a key agronomic trait for assessing rice growth and predicting grain yield. However, conventional measurement methods are labor-intensive and inefficient. This study develop a robust, automated system for estimating rice canopy coverage by comparing traditional image analysis techniques with deep learning-based semantic segmentation models. The methodologies compared were: (1) five traditional vegetation index-based methods and (2) five mainstream convolutional neural network (CNN)-based semantic segmentation models (i.e., U-net, DeepLabV3+, LinkNet, FPN, PSPNet), each implemented with a ResNet-101 backbone. A large-scale dataset of 5,000 RGB images captured from 18 locations across Korea was constructed for training and validation. Deep learning-based models significantly outperformed the vegetation index methods. Among the CNN models, U-net achieved the highest performance with a mean Intersection over Union (mIOU) of 0.986. This study identifies U-net architecture as an optimal methodology for automated and highly accurate canopy coverage analysis and establishes a foundational technology for advancing high-throughput phenotyping in precision agriculture. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparison of Deep Learning and Vegetation Index Methodologies for Estimating Rice Canopy Coverage Based on RGB Images
-
Original Research Article
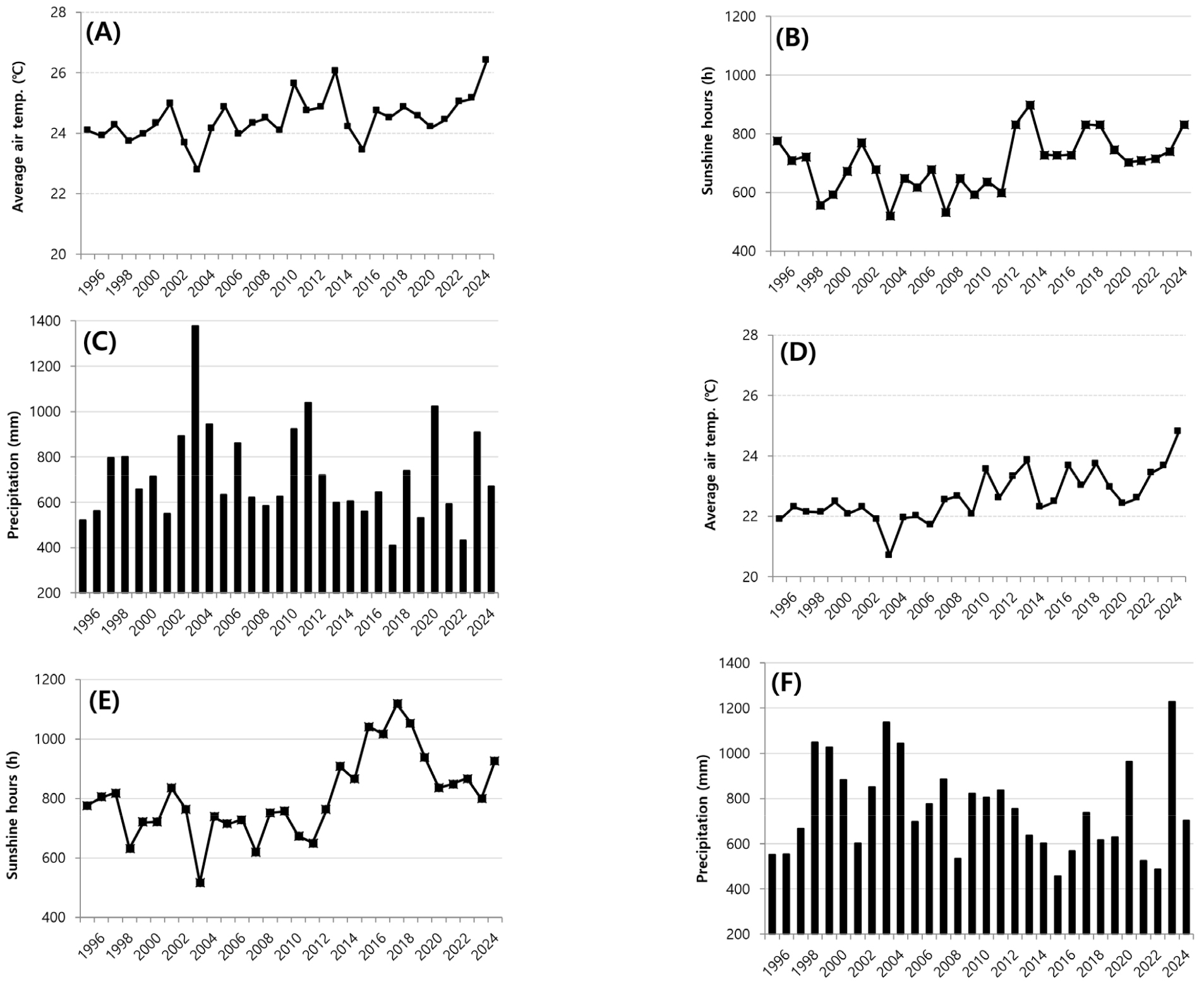
-
Climatic Factors Associated with Yield Variation of Rice Cultivar ‘Ilpum’ in the Inland Region of Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea
경북 내륙 지역 일품벼 수량 변화와 기상 요인의 상관성 분석
-
Suhyeon Heo, Jong-Hee Shin, Young-Un Song, Jong-Do Cheung, Jun-Hong Park
허수현, 신종희, 송영운, 정종도, 박준홍
- This study investigated the long-term yield performance of the major rice cultivar ‘Ilpum’ in the inland region of Gyeongsangbuk-do and identified climatic …
- This study investigated the long-term yield performance of the major rice cultivar ‘Ilpum’ in the inland region of Gyeongsangbuk-do and identified climatic factors influencing its productivity. Yield data from experimental fields in Daegu (1995-2024, 30 years) and Andong (2001-2024, 24 years), where ‘Ilpum’ was cultivated under identical management practices, were analyzed together with agro-meteorological records from the Korea Meteorological Administration. Over the past three decades, precipitation decreased in both regions, while sunshine duration increased and temperatures exhibited a consistent upward trend. In Daegu, maximum temperature rose markedly during the vegetative stage, whereas changes during the grain-filling stage were relatively moderate, limiting yield reduction. In contrast, Andong experienced greater temperature increases throughout the growing season, with particularly pronounced rises in mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures during the reproductive stage. Yield component analysis indicated that the number of panicles per hill was the primary determinant in Daegu, while an earlier heading date played a critical role in Andong. Correlation analysis further revealed that in Daegu, sunshine duration during the grain-filling stage and temperature during the vegetative stage were strongly associated with yield, whereas in Andong, both temperature and sunshine duration during the vegetative and reproductive stages showed strong relationships. Across both sites, rice yield was positively correlated with sunshine duration, while the grain-filling ratio was closely related to maximum temperature and sunshine duration during the grain-filling stage. These findings underscore the importance of temperature and solar radiation in determining rice productivity in inland regions and can serve as a basis for developing strategies to stabilize yield and grain quality of rice cultivation under climate change conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Climatic Factors Associated with Yield Variation of Rice Cultivar ‘Ilpum’ in the Inland Region of Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea
-
Original Research Article
-
Machine Learning Analysis of Rice Quality and Palatability Evaluation Data to Predict Rice Taste and Interpret Variables
쌀 품질 및 기호도 평가 데이터의 머신러닝 분석을 통한 밥맛 예측 및 변수 해석
-
Yuchan Choi, Hyun-jin Park, Yu-geun Oh, Ji-eun Kwak
최유찬, 박현진, 오유근, 곽지은
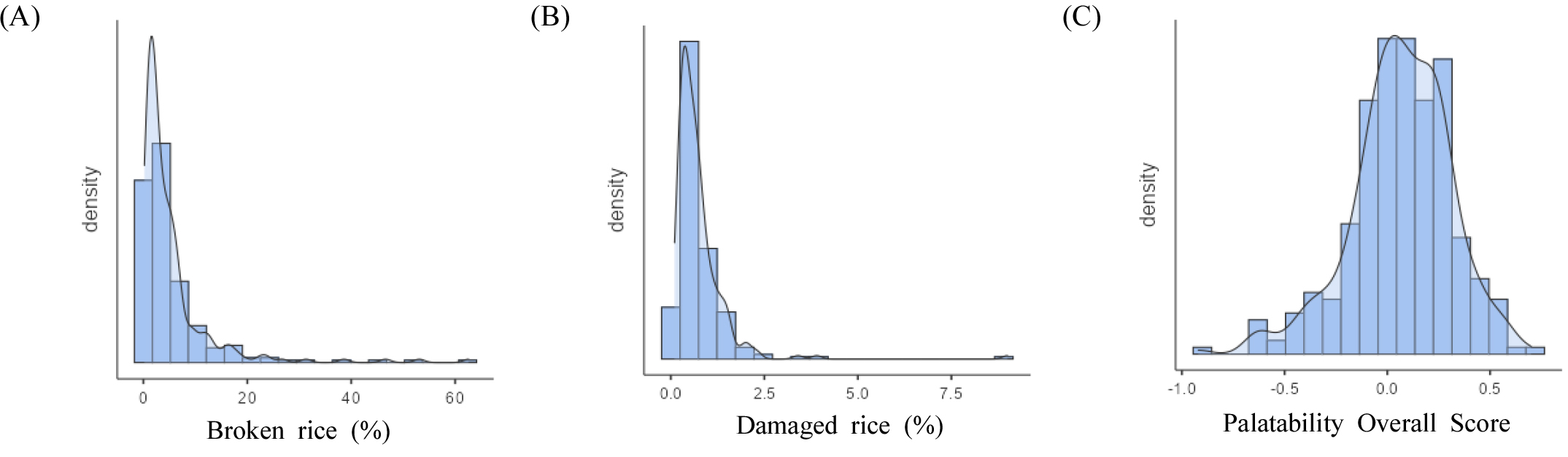
- This study aimed to develop a machine learning-based evaluation framework for predicting rice (Oryza sativa L.) eating quality using physicochemical and …
- This study aimed to develop a machine learning-based evaluation framework for predicting rice (Oryza sativa L.) eating quality using physicochemical and sensory datasets accumulated over the past decade at the National Institute of Crop Science (NICS). A total of 297 rice samples were collected, including grain shape, milling, and physicochemical traits, along with sensory panel scores of overall palatability. After data preprocessing and the removal of outliers, 216 samples were used for model training. Principal component analysis (PCA), cluster analysis, and preference mapping were conducted to identify the structural relationships among rice quality traits. Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) and Random Forest models were then trained to classify overall eating quality into two categories (A: superior, B: inferior). Model performance was evaluated using five-fold cross-validation and an independent test set. The Random Forest model achieved the highest accuracy (0.7143) and Kappa coefficient (0.4273), indicating statistically significant generalization performance (p = 0.009). SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis revealed that amylose, protein, and Milled/Brown Ratio were the most influential predictors of eating quality, where lower amylose and protein content and higher Milled/Brown Ratio contributed positively to superior eating quality (A). These results demonstrate the potential of machine learning as a complementary approach to sensory testing by enhancing objectivity and efficiency, and suggest core quality indices for rice breeding and processing—namely, amylose, protein, and Milled/Brown Ratio. - COLLAPSE
-
Machine Learning Analysis of Rice Quality and Palatability Evaluation Data to Predict Rice Taste and Interpret Variables
-
Original Research Article
-
Development of Rice Pre-harvest Sprouting Rate Measurement Program Using YOLOv8 Deep Learning Model
YOLOv8 딥러닝 모델을 이용한 벼 수발아율 측정 프로그램 개발
-
Soojin Jun, Younguk Kim, Myeongjin Kang, Mi Hyun Cho, Hyoja Oh, HwangWeon Jeong, Jae Il Lyu, Jeongho Baek, Seon-Hwa Bae, Hongro Lee, Hyeonso Ji
전수진, 김영욱, 강명진, 조미현, 오효자, 정황원, 유재일, 백정호, 배선화, 이홍로, 지현소
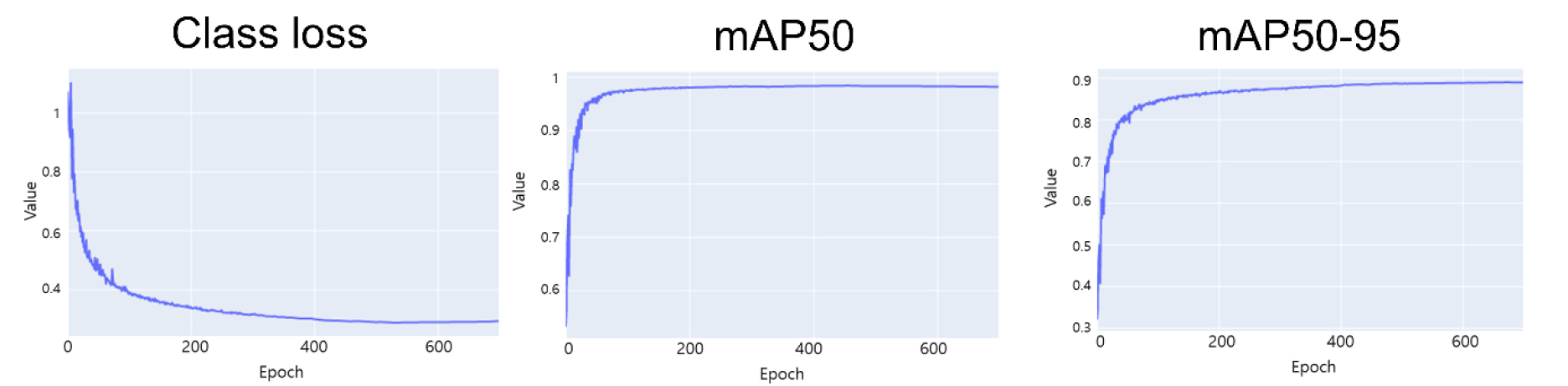
- Pre-harvest Sprouting (PHS) in rice is a critical agronomic problem that significantly reduces grain yield and quality. Conventional PHS measurement relies on …
- Pre-harvest Sprouting (PHS) in rice is a critical agronomic problem that significantly reduces grain yield and quality. Conventional PHS measurement relies on manual visual inspection, which is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to assessor bias, rendering it unsuitable for high-throughput phenotyping. In this study, we developed a computer-based program for the automated measurement of PHS and seed germination rate. This program integrates a deep learning model for detecting germinated and ungerminated rice seeds and a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI). A dataset of 132,200 seed images, produced under diverse background colors, was used for training the deep learning model. The optimized model achieved a mean average precision at IoU 0.5 (mAP50) of 0.987 and an mAP50-90 of 0.916, demonstrating a robust performance under varying imaging conditions. The developed GUI facilitates key functions, including image loading, single and batch detection, visualization of detection results, automatic calculation of PHS and germination rates, and exporting of data. To assess the reliability of the method, PHS rates measured using threshed rice seeds were compared against those of conventional measurement methods using unthreshed rice seeds across 20 rice cultivars. A strong positive correlation (R2 = 0.8909) demonstrated that the proposed image analysis approach using threshed seeds serves as a reliable alternative to the conventional manual method using unthreshed rice seeds. The program developed in this study is convenient to use and significantly enhances the reproducibility and efficiency of rice PHS and germination rate measurement, thereby enabling streamlined phenotyping for rice breeding programs and other rice research. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of Rice Pre-harvest Sprouting Rate Measurement Program Using YOLOv8 Deep Learning Model
-
Original Research Article
-
Assessment of Seedling Growth and Seed Utilization Potential of ‘Baromi2’ at Reduced Germination Rate
‘바로미2’ 발아율 저하에 따른 어린모 생육 특성 및 종자 활용 가능성 평가
-
Jaekyeong Baek, Seoyoung Yang, Yu-na Kim, Yeong-Seo Song, Sugwon Roh, Miok Um, Jung-Il Cho, Wunha Hwang, Jiyoung Shon
백재경, 양서영, 김유나, 송영서, 노석원, 엄미옥, 조정일, 황운하, 손지영
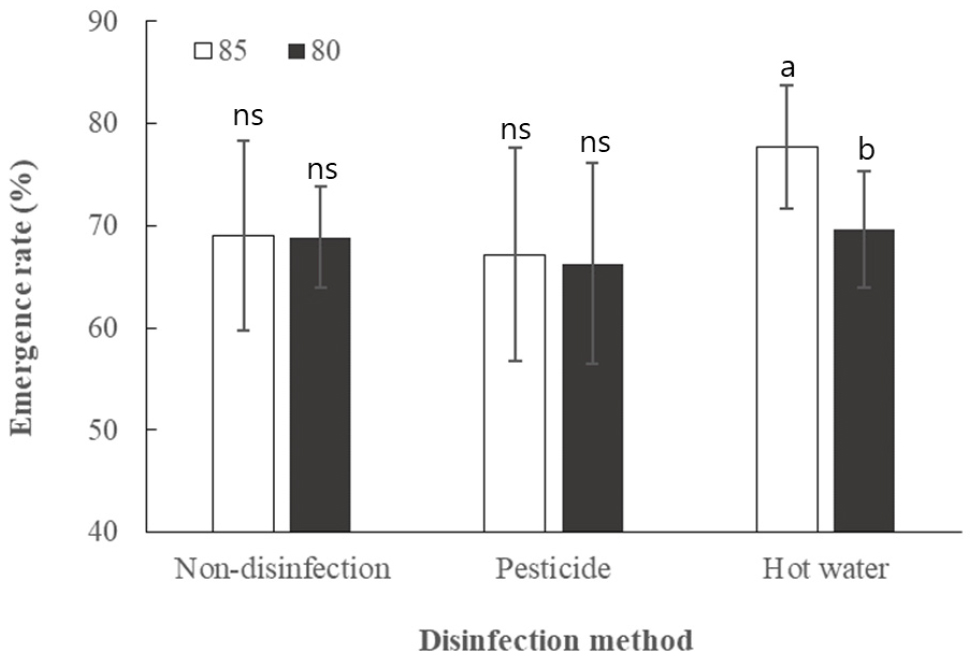
- Climate change-induced temperature increases have led to frequent heat stress during the rice grain-filling stage, resulting in reduced starch accumulation, higher rates …
- Climate change-induced temperature increases have led to frequent heat stress during the rice grain-filling stage, resulting in reduced starch accumulation, higher rates of immature or pre-germinated grains, and reduced in seed germination and vigor.‘Baromi2’, a floury rice cultivar, is particularly susceptible to pre-harvest sprouting even under relatively low cumulative ripening temperatures. Because of severe heat conditions during the 2024, seed quality deterioration prompted consideration of temporarily lowering germination standard for ‘Baromi2’ from 85% to 80%. This study evaluated how reduced germination level influences early seedling performance and identified a suitable seed disinfection and water management method for stable nursery production. Seven seed lots produced in 2024 from three regions were tested. Appearance analysis of brown rice showed that seeds with 80% germination had lower perfect grain ratios and higher immature and damaged grain proportions compared with 85% germination seeds. Seedling growth was assessed after applying three treatments: non-disinfection, chemical treatment, and hot-water treatment. Hot-water treatment significantly reduced emergence in 80% germination seeds, showing an 8% point decrease compared with 85% seeds, whereas chemical treatment maintained stable seedling establishment except in lots with high immature grain ratios. Under high-temperature nursery conditions (27°C), continuous flooding increased seedling height by approximately 5.5% compared with standard irrigation, indicating a greater risk of elongation, however germination rates had no significant effect on seedling establishment. Overall, stable seedling production is feasible even when germination decreases to 80%; however, hot-water disinfection should be avoided, and careful water management is required to prevent excessive elongation under high-temperature nursery conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessment of Seedling Growth and Seed Utilization Potential of ‘Baromi2’ at Reduced Germination Rate
-
Original Research Article
- Identification of Major QTLs Conferring Rice Blast Resistance Using an SNDH Population
- Dan-Dan Zhao, Hyunjung Chung, Muhammad Farooq, Nam-Gu Kim, Bo-Seong Seo, Soo Yeon Choi, Shinhwa Kim, Sang-Min Kim, Jang-Ho Lee, Xiao-Xuan Du, Kyung-Min Kim
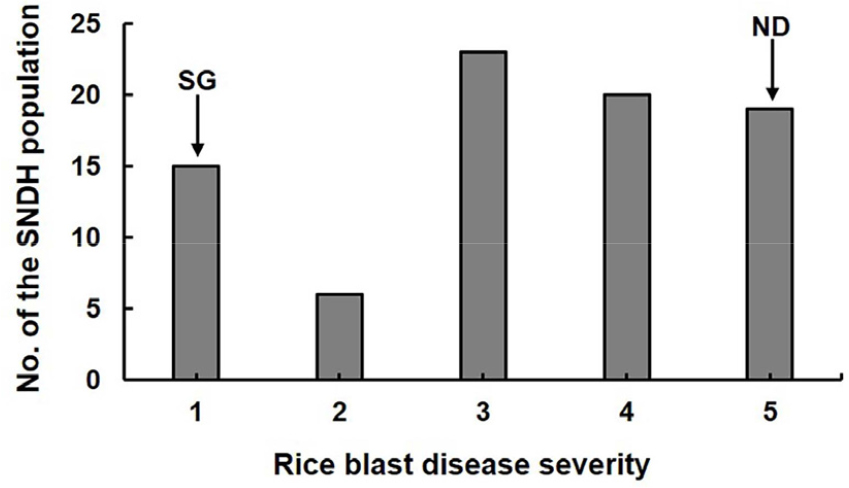
- The rice blast pathogen, Magnaporthe oryzae, remains a significant threat to global rice production, often causing substantial yield losses in regions with …
- The rice blast pathogen, Magnaporthe oryzae, remains a significant threat to global rice production, often causing substantial yield losses in regions with favorable environmental conditions. Given the limitations of chemical control and the rapid evolution of pathogen populations, developing rice varieties with durable and broad-spectrum blast resistance is crucial for long-term disease management and reducing the overall impact on rice cultivation. To address this need, a qualitative trait locus (QTL) analysis was performed using a set of representative Korean isolates and a ‘Samgang/Nagdong’ doubled haploid (SNDH) population to identify key loci associated with rice blast resistance. Two major and significant loci, qrbr2 (chromosome 2; RM318–s2038) and qrbr6 (chromosome 6; s6015–s6018), were detected with LOD values of 4.13 and 5.15, accounting for 44% and 43% of the phenotypic variation, respectively. Among the candidate genes within these regions, Os02g0674700 (Osrbrq2), which shares a strong homology with RING-type E3 ubiquitin protein ligases, has emerged as a promising gene that contributes to resistance within the qrbr2 locus. These findings underscore the importance of qrbr2 and qrbr6, along with the Osrbrq2 candidate gene, in shaping rice defense responses, and provide a valuable basis for further characterization and marker-assisted breeding to enhance rice blast resistance. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Research Article
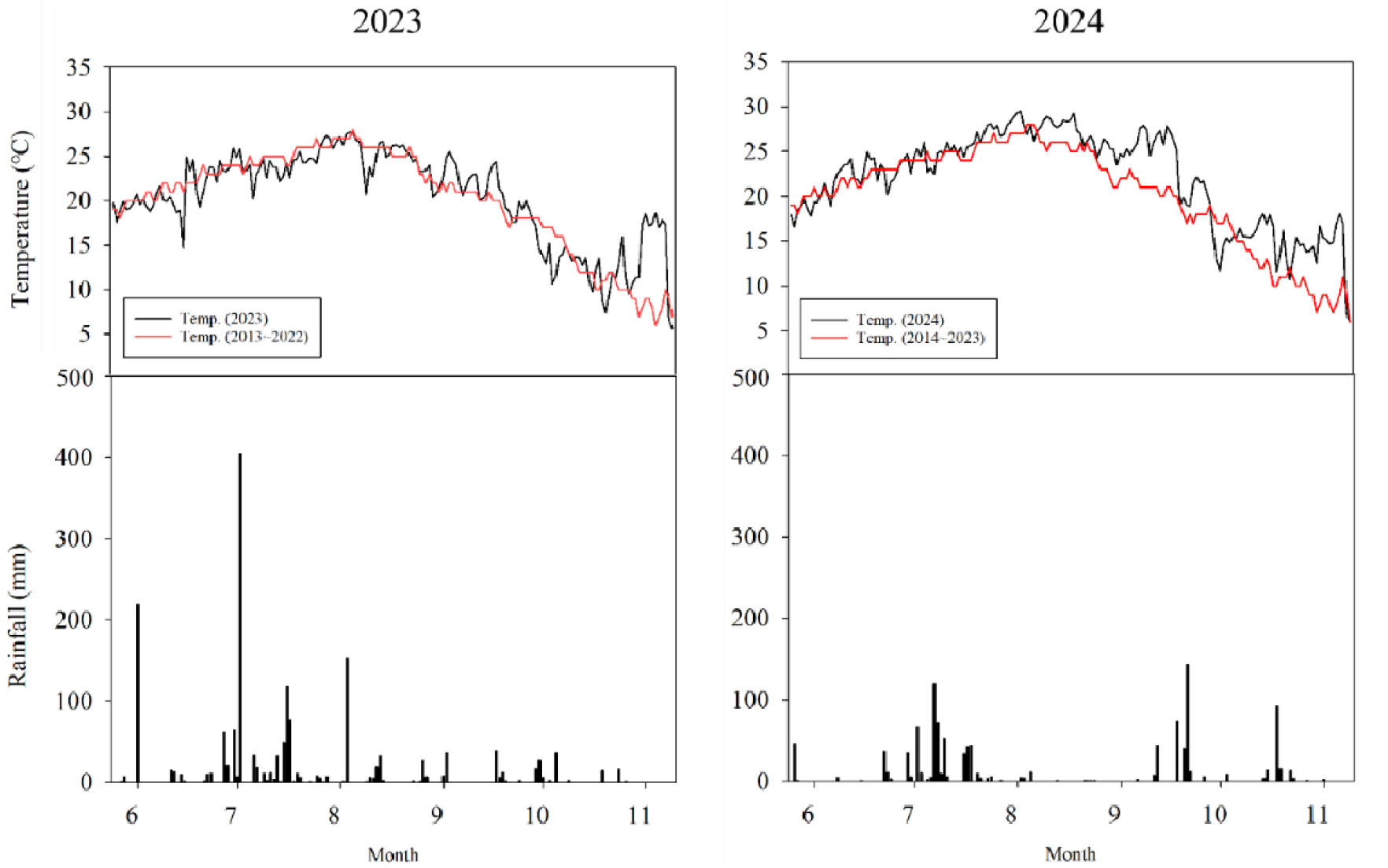
-
Effects of Cumulative Temperature on Growth and Yield of Mid–Late Maturation Soybean by Sowing Time in Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea
충북지역 파종시기별 적산온도에 따른 중만생종 콩의 생육과 수량
-
Jeong-Min Lee, Bo-yun Lee, Min-ji Kim, Jwakyung Sung
이정민, 이보윤, 김민지, 성좌경
- This study was conducted to provide informed climate change adaptation strategies by analyzing the effects of sowing date on soybean growth and …
- This study was conducted to provide informed climate change adaptation strategies by analyzing the effects of sowing date on soybean growth and yield in Chungcheongbuk-do (North Chungcheong), Korea—with particular attention to how cumulative temperature influences crop development—and propose an optimal sowing window. Two mid–late maturing soybean cultivars for soy-paste, namely Daewonkong and Seonpung, were evaluated over two years (2023-2024) at field elevations of 163 m and 234 m, respectively. Four sowing dates were tested: late May, early June, mid-June, and late June. For late May sowing, the growing period and cumulative temperature averaged 160 days and 3,541°C, respectively; both metrics declined as sowing was delayed, reaching 124 days (-22.5%) and 2,845 °C (-19.7%), respectively, for late June sowing. Growth traits measured at R2 stage (full bloom) and R5 stage (beginning seed) were greatest with late May sowing and decreased significantly for delayed sowing. The highest yields were obtained for early June sowing, reaching 420 and 547 kg 10a-1 for Daewonkong and Seonpung, respectively. Yield showed a strong positive correlation with pods per plant (r = 0.91***), which in turn was positively associated with cumulative temperature (r = 0.74**). These results indicate that soybean yield is indirectly influenced by cumulative temperature through its effects on intermediate growth traits. Considering both yield and agronomic characteristics, early June is identified as the optimal sowing time for Chungcheongbuk-do. Nevertheless, further research is needed to determine the optimal sowing window when seed quality—including protein content in paste soybeans—is taken into account. - COLLAPSE
-
Effects of Cumulative Temperature on Growth and Yield of Mid–Late Maturation Soybean by Sowing Time in Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea
-
Original Research Article
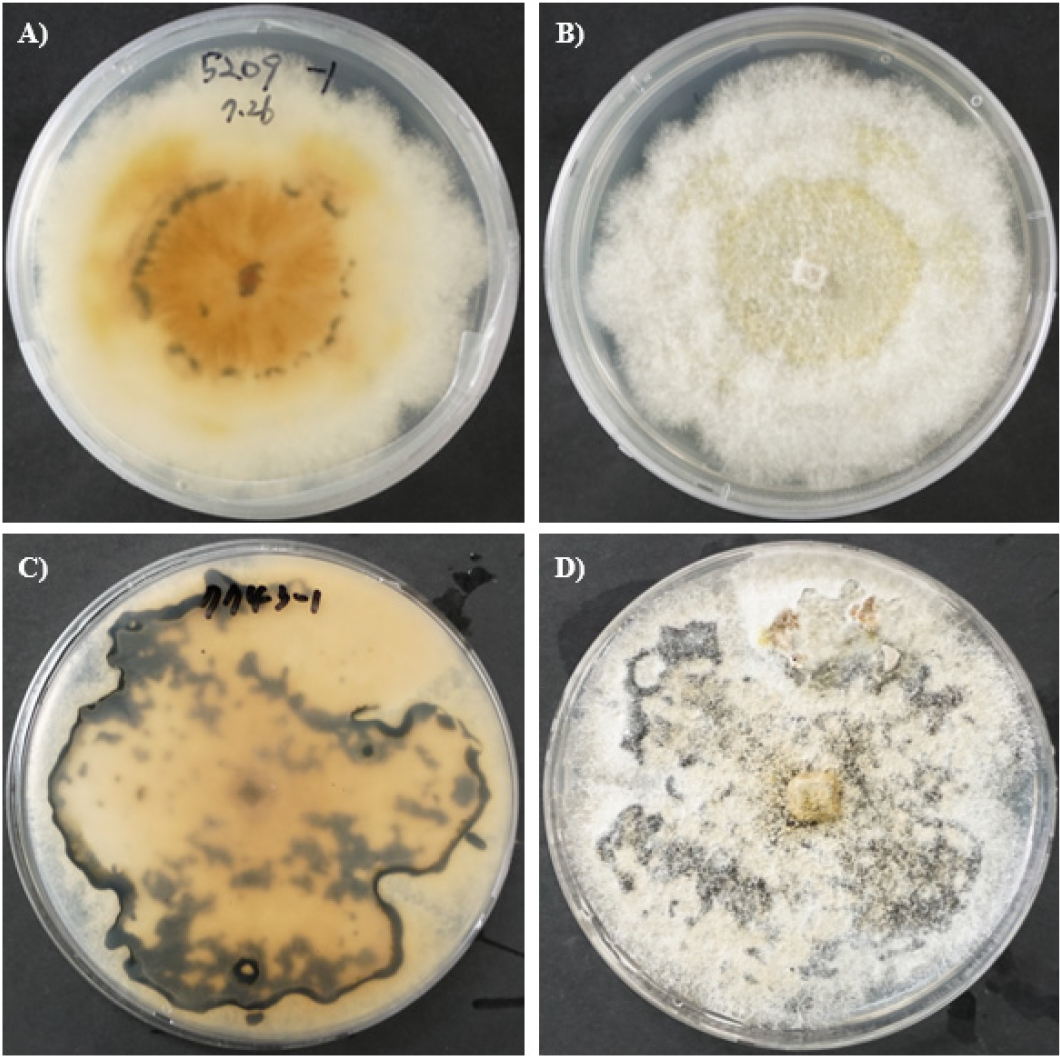
- A Rapid In Vitro Seedling Assay for Screening Soybean Resistance to Diaporthe longicolla
- Guta Rahel Dinsa, Jun Hyoung Jeon, Hyeon Su Lee, Seoyeon Hong, Ok Jae Won, Maharjan Rameswor, Youngnam Yoon, Yun-Woo Jang
- Pod and stem blight, primarily caused by Diaporthe longicolla, is a major disease affecting soybean production worldwide. Accurate and efficient evaluation …
- Pod and stem blight, primarily caused by Diaporthe longicolla, is a major disease affecting soybean production worldwide. Accurate and efficient evaluation of disease resistance in soybean cultivars strongly depends on the inoculation technique used. Eight artificial inoculation methods were compared, including cut-seedling, toothpick, stem wound, mycelium contact, mycelium spraying, spore injection, conidial suspension injection, and ascospore inoculation methods, using two virulent D. longicolla isolates on two soybean varieties under controlled conditions. The stems and leaves of three-week-old soybean seedlings were inoculated using the above-mentioned techniques. Disease severity, lesion length, and area under the disease progress curve (AUDPC) were used to assess pathogenicity and disease development. The results revealed differences among inoculation methods, isolates, and soybean varieties. The cut-seedling, toothpick, and stem wound methods consistently induced earlier and more severe symptoms, the highest AUDPC values, and even plant death in some cases. In contrast, the ascospore and mycelium spraying methods produced negligible or no symptoms. The findings highlight the critical influence of the selected inoculation technique on disease expression, providing valuable guidance for optimizing disease resistance screening and pathogenesis studies in soybean breeding programs. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Research Article
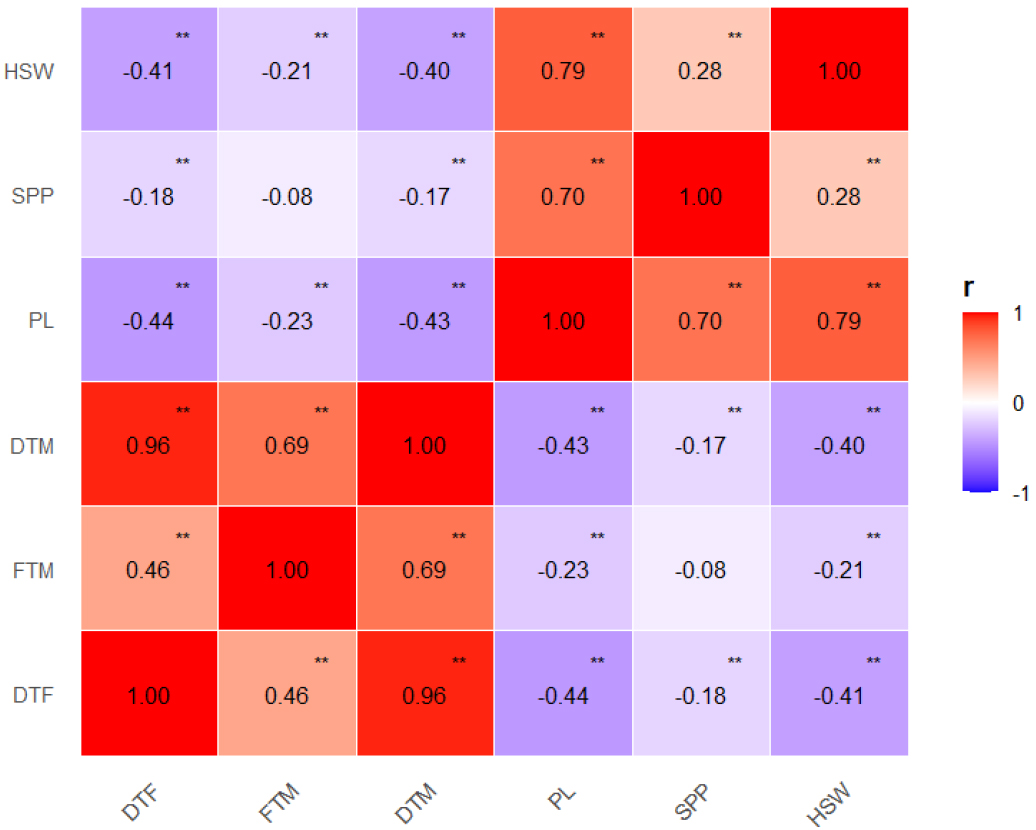
-
Multivariate Cluster Analysis of Quantitative Traits in Korean and Foreign Mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek] Germplasm
국내외 녹두 유전자원의 양적형질 변이 및 다변량 군집분석
-
Yu-Na Kim, Eun Soo Lee, Seoyeong Yang, Jaekyeong Baek, Youngseo Song, Woon-Ha Hwang, Sukown Park
김유나, 이은수, 양서영, 백재경, 송영서, 황운하, 박수권
- Mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek] originated in the region of the Indian subcontinent and is currently cultivated mainly in Central, …
- Mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek] originated in the region of the Indian subcontinent and is currently cultivated mainly in Central, East, and Southeast Asia. Although mungbean has high adaptability and nutritional value, and thus considerable potential for cultivation in diverse environments, the genetic resources available for breeding remain limited. In this study, we evaluated the phenotypic variation and multivariate structure of 477 mungbean germplasm accessions collected from 12 countries, including Korea. Statistical analyses revealed that Korean accessions are characterized by a shorter growth duration (representing an early-maturing phenotype), and have longer pod lengths, larger numbers of seeds per pod, and higher 100-seed weights than foreign accessions, thereby indicating efficient pod development and seed filling, even within a limited growth period. Principal component analysis based on an assessment of six traits revealed that the first two principal components (PC1, PC2) explained 78.22% of the total variation. PC1, showing a positive association with flowering time and negative association with pod and seed size, partially differentiated Korean from foreign accessions. K-means clustering analysis identified three distinct clusters, among which Cluster III was characterized by both early maturity (days to flowering: 45.4, days to maturity: 64.03) and high yield potential (pod length: 11.18 cm, 100-seed weight: 5.9 g), indicating its suitability as breeding material under Korean cultivation conditions. These findings provide valuable insights into the phenotypic diversity of global mungbean germplasm and fundamental information for the breeding of varieties adapted to domestic environments. - COLLAPSE
-
Multivariate Cluster Analysis of Quantitative Traits in Korean and Foreign Mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) R. Wilczek] Germplasm
-
Original Research Article
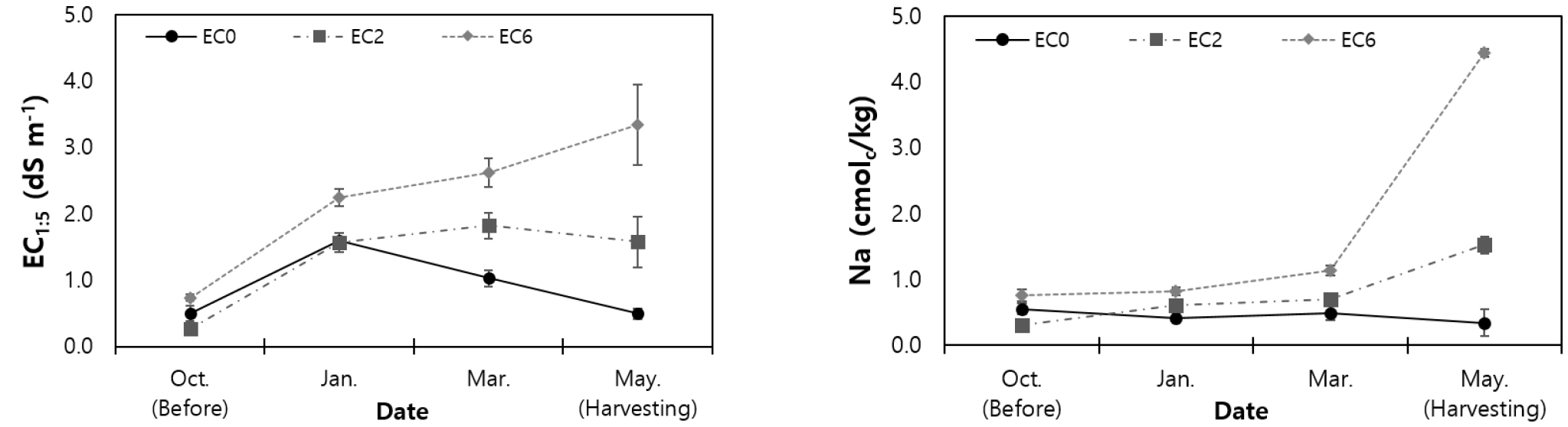
-
Growth and Yield Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Irrigation Water Salinity Levels in the Saemangeum Reclamation Area
새만금간척지에서 관개수 염농도에 따른 밀 품종별 생육 및 수량 반응
-
Hee-Kyoung Ock, Seo-Young Jeong, Hyeon-soo Jang, Eun Ji Suh, Yang-Yeol Oh, Hyun-Suk Jo, Bang-Hun Kang
옥희경, 정서영, 장현수, 서은지, 오양열, 조현숙, 강방훈
- Reclaimed land often limits wheat productivity due to salinity. This study evaluated varietal suitability and a practical salinity threshold for stable production. …
- Reclaimed land often limits wheat productivity due to salinity. This study evaluated varietal suitability and a practical salinity threshold for stable production. The experiment was conducted using three wheat cultivars: Beakkang, Jokyeong, and Seaguemkang. Irrigation water salinity was controlled at ECw levels of 0, 2, and 6 dS m-1. Root-zone soils were monitored from pre-sowing to harvest. Saline irrigation increased soil 1:5 extract electrical conductivity (EC1:5) and exchangeable Na+. By March, plant height and stem number were significantly affected by salinity and cultivar; under EC6, stem number decreased by at least 20% relative to the control across all cultivars. Yield correlated negatively with soil EC1:5 and exchangeable Na+ and positively with dry mass, stems m-2, and grains per spike; the strongest association was with grains per spike (r=0.89). Principal component analysis showed salinity indicators loading opposite to yield-related traits on PC1 (≈43% variance), separating EC0, EC2, and EC6 along this axis. Across treatments, Seaguemkang achieved the highest absolute yields (≈515/390/210 kg 10a-1 at EC0/EC2/EC6). Linear fits of relative yield to ECw produced decline rates (% per dS m-1) of –2.0, –9.5, and –9.7 for Beakkang, Jokyeong, and Seaguemkang (R²=0.83–0.99). Despite a steeper decline, Seaguemkang maintained the greatest yield level; its EC70 (70% relative yield) was approximately 2.9 dS m-1. The results underscore the importance of maintaining effective tiller number and grains per spike under salinity. Among the tested cultivars, Seaguemkang appears particularly suitable for reclaimed fields when irrigation ECw is controlled below about 3 dS m-1. - COLLAPSE
-
Growth and Yield Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to Irrigation Water Salinity Levels in the Saemangeum Reclamation Area
-
Original Research Article
-
Prediction of Wheat Milling Yield Using Machine Learning: Identification of Seed Traits Associated with Milling Performance
기계학습 기반 밀 제분율 예측 및 연관 종자 형질 규명
-
Myoung-Goo Choi, Go Eun Lee, Jinhee Park, Chang-Hyun Choi, Jae-Han Son, Junseok Choi, Yurim Kim, Sukjin Kim, Chon-Sik Kang, Jeong-Heui Lee
최명구, 이고은, 박진희, 최창현, 손재한, 최준석, 김유림, 김숙진, 강천식, 이정희
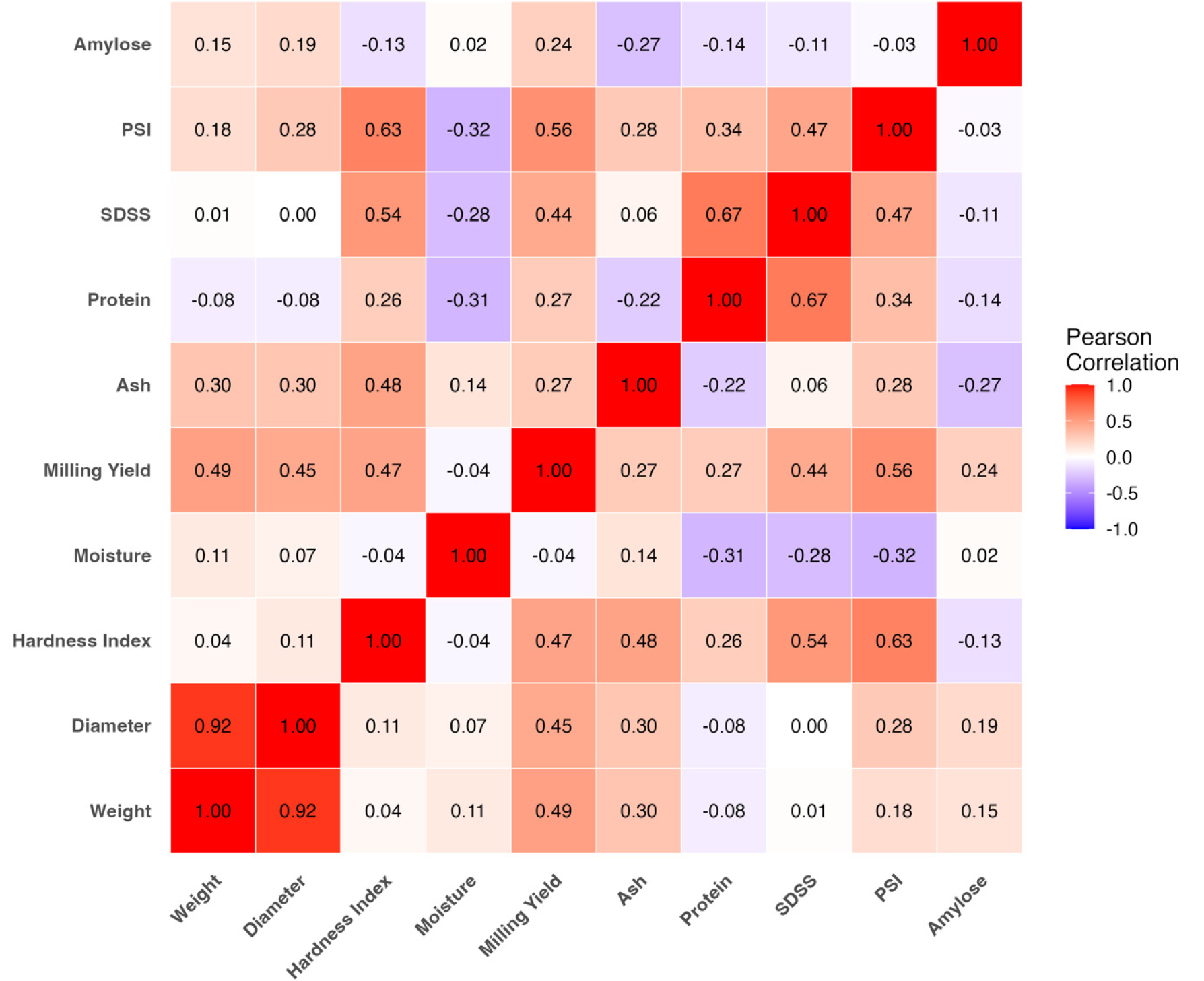
- Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a cornerstone of global food security, and improving milling yield is vital for enhancing processing efficiency …
- Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is a cornerstone of global food security, and improving milling yield is vital for enhancing processing efficiency and the economic value of grain-based industries. However, milling yield is a multifactorial trait governed by complex interactions among physical and chemical kernel properties, which are often inadequately captured by conventional linear models. In this study, a machine learning framework based on the Random Forest (RF) regression algorithm was established to predict milling yield and to quantify the relative contribution of kernel attributes. Forty-five Korean wheat cultivars were evaluated for key physical traits (kernel weight, hardness, and particle size) and chemical traits (protein, ash, and amylose contents). The RF model achieved a high predictive accuracy (R2 = 0.94; RMSE = 1.341), demonstrating its robustness in modeling the non-linear relationships among grain traits. Variable importance and partial dependence analyses identified kernel hardness, particle size, and kernel weight as the most influential predictors of milling yield, while protein and ash contents exerted relatively minor effects. A distinct non-linear response was detected in the hardness range of 25–40, where milling yield increased sharply before reaching a plateau. Principal component and cluster analyses further grouped cultivars into four distinct clusters according to trait combinations, underscoring that milling performance is determined by multivariate interactions rather than single trait effects. Collectively, this RF-based analytical framework provides a data-driven approach for integrating complex quality traits into wheat breeding and selection programs, thereby supporting the development of high-yielding and quality-stable Korean wheat cultivars optimized for milling performance. - COLLAPSE
-
Prediction of Wheat Milling Yield Using Machine Learning: Identification of Seed Traits Associated with Milling Performance
-
Original Research Article
-
Development of Post-harvest Management Technology for Anthocyanin Production in the Husk of the New Purple Corn Hybrid Variety ‘Saekso 5’
자색옥수수 신품종 ‘색소5호’ 포엽 안토시아닌 생산을 위한 수확 후 관리기술 개발
-
Min Namgung, Ki Yeon Lee, Si Hwan Ryu, Jae Keun Choi, Hee Sun Noh, Jung Heon Han, Seung Hyeon Wang, Hye Rim Choi, Yong Jin An, Hee Yeon Kim
남궁민, 이기연, 류시환, 최재근, 노희선, 한정헌, 왕승현, 최혜림, 안용진, 김희연
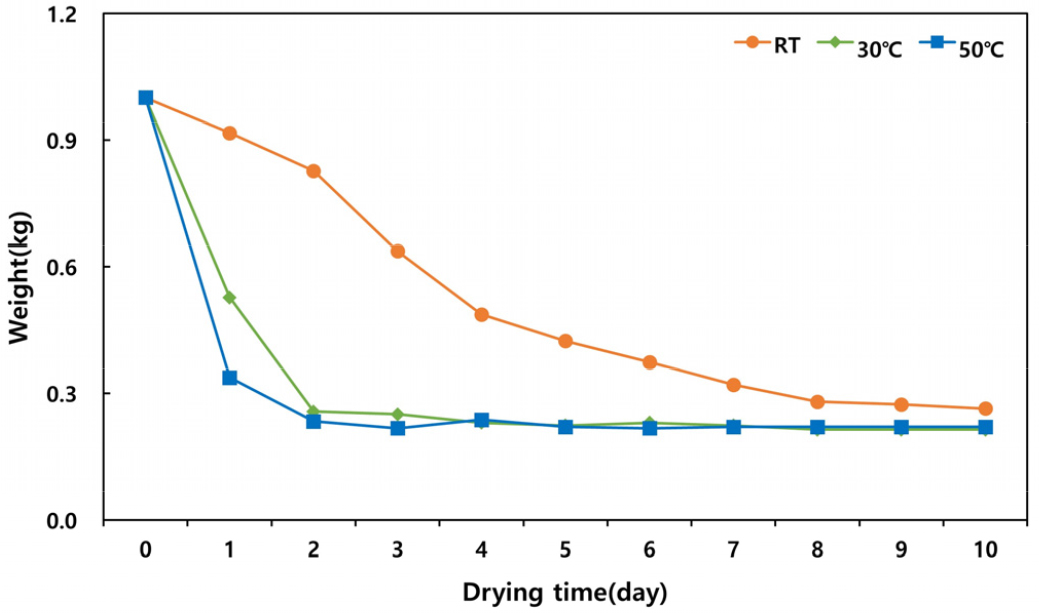
- This study determined the optimal drying and storage conditions, which are regarded as crucial post-harvest management technologies, for the production of high-quality …
- This study determined the optimal drying and storage conditions, which are regarded as crucial post-harvest management technologies, for the production of high-quality husk of ‘Saekso 5’. To determine changes in the quality characteristics of the husk according to drying temperature, samples were dried at 30°C, 50°C and room temperature (RT). Samples dried at 50°C remained free from fungal contamination, whereas the quality of samples dried at 30°C and RT significantly decreased due to fungal infection. Except for moisture, there was no difference in general component content between samples dried at 30°C and 50°C. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in Cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G) content, which is the husk’s main quality indicator. The storage test was conducted at three different temperatures (-5°C, 5°C and RT) for six weeks. Zearalenone mycotoxin levels exceeding safe intake limits were detected after two weeks in samples stored at RT; but samples stored at low temperatures were not contaminated with fungi. Quality analysis according to storage temperature showed that the moisture content at -5°C was changed less than that at 5°C, while the C3G content was maintained for up to one week. Therefore, to produce high-quality husk of ‘Saekso 5’, a drying temperature of 50°C is more effective than 30°C. If post-harvest storage is required, the husk can be stored at -5°C for up to one week. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of Post-harvest Management Technology for Anthocyanin Production in the Husk of the New Purple Corn Hybrid Variety ‘Saekso 5’
-
Original Research Article
-
Changes in Growth, Yield, and Vegetation Indices of Potato under Different Drought Stress Intensities
수분 스트레스 강도에 따른 감자의 생육·수량 및 식생지수 변화
-
In-ha Lee, Dong-won Kwon, Sung-yul Chang, Woo-jin Im, Wan-Gyu Sang, Hyeok-jin Bak, Do-Hyun Kim, Jung-Il Cho, Nam-Jin Chung, Woon-Ha Hwang
이인하, 권동원, 장성율, 임우진, 상완규, 박혁진, 김도현, 조정일, 정남진, 황운하
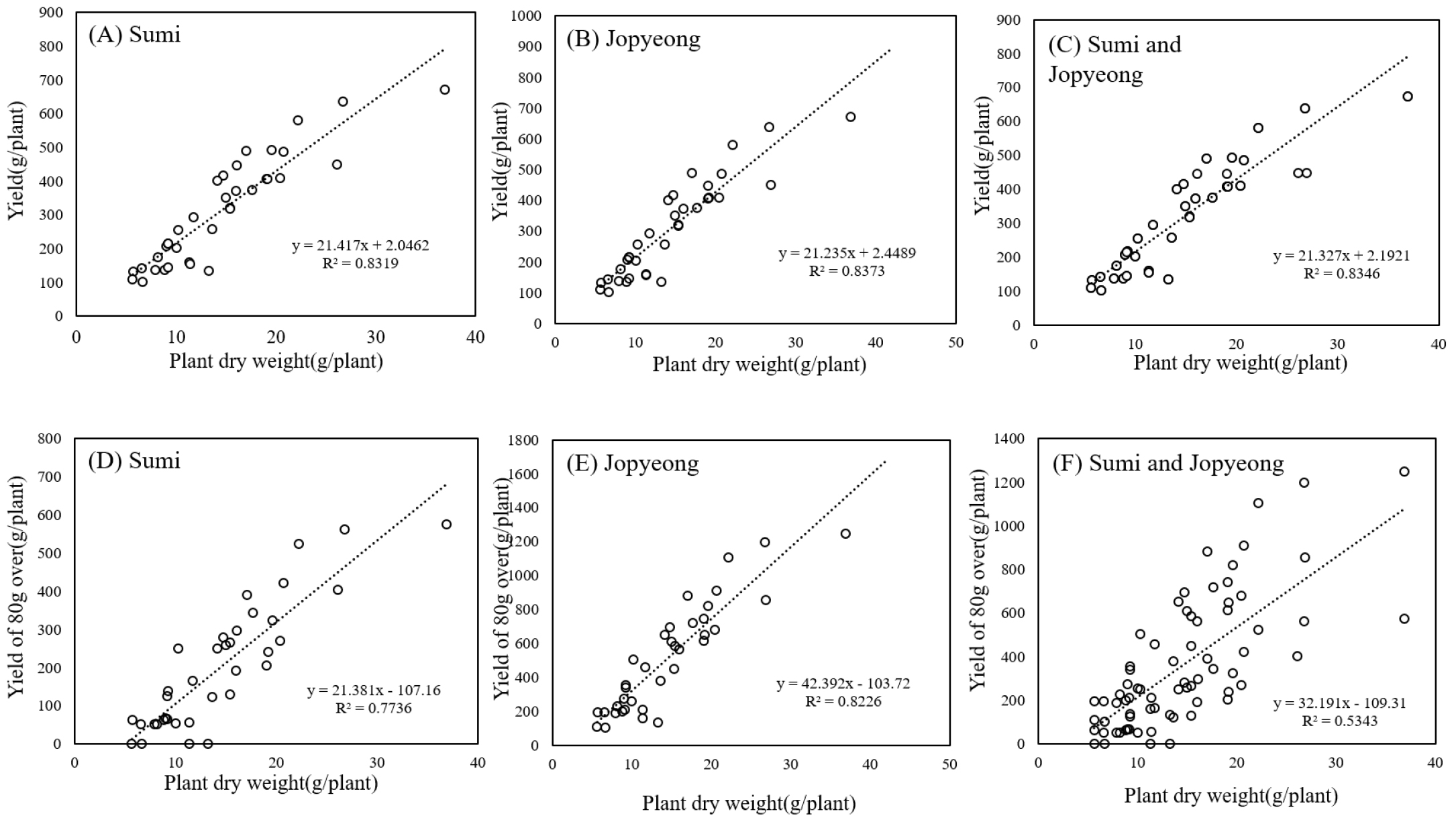
- Recent climate change has increased rainfall irregularity and drought frequency during the spring potato growing season in Korea, raising concerns over yield …
- Recent climate change has increased rainfall irregularity and drought frequency during the spring potato growing season in Korea, raising concerns over yield stability. This study aimed to analyze the growth, yield, and physiological responses of two early-maturing potato cultivars, namely “Sumi” and “Jopung,” under precisely controlled drought conditions. Plants were grown in a rain-out shelter using an automated drip irrigation system, and various soil moisture levels were imposed. As soil moisture decreased, both cultivars showed reductions in plant height and leaf number. Aboveground dry weight, total yield, and marketable yield decreased significantly with increasing drought severity, and strong correlations (R² > 0.95) were observed between aboveground biomass and yield. Leaf spectral indices also responded sensitively to drought stress: NDVI and CRI1 decreased, reflecting reduced physiological activity and carotenoid-associated photoprotection, whereas FRI increased due to stress-induced flavonol accumulation. These results demonstrate the potential of portable leaf spectroscopy as a non-destructive phenotyping tool for assessing drought responses and predicting potato yield, particularly in controlled environments, such as greenhouses, where the application of remote sensing is limited. - COLLAPSE
-
Changes in Growth, Yield, and Vegetation Indices of Potato under Different Drought Stress Intensities
-
Original Research Article
-
Assessing the Potential of Potato Yield Estimation using the In-season Normalized difference Vegetation Index
감자 생육기 NDVI 분석 기반 수량 예측 가능성 분석
-
Woon-Ha Hwang, In-Ha Lee, Seng-Yul Jang, Dong-Won Kwon, Woo-Jin Im, Hyeok-Jin Park, Wan-Gue Sang, Do-Hyen Kim, Un-Ji Kim
황운하, 이인하, 장성율, 권동원, 임우진, 박혁진, 상완규, 김도현, 김은지
- Estimating potato production before harvest is necessary for stabilizing the distribution structure and securing storage space. Overseas, active research is underway using …
- Estimating potato production before harvest is necessary for stabilizing the distribution structure and securing storage space. Overseas, active research is underway using a recently developed sensing technology to analyze the growth of above-ground potatoes, but not much related research has been undertaken in Korea. To diagnose potato yield using the vegetation index, the correlation between above-ground dry weight, yield, and the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) was analyzed. The above-ground dry weight showed a significant correlation with the total potato yield, but its correlation with the yield of potatoes weighing 80 g for more was low, which affects marketability. The above-ground dry weight of potatoes showed a significant correlation with the NDVI at the period of greatest growth, whereas the correlation coefficient tended to decrease as the harvest season approached. Potato yield shows a significant correlation with the NDVI at the period of greatest growth; therefore, the final potato yield can be predicted and diagnosed through the vegetation index at the peak of growth. - COLLAPSE
-
Assessing the Potential of Potato Yield Estimation using the In-season Normalized difference Vegetation Index
-
Original Research Article
-
Optimizing Early Transplanting and Harvesting Dates for ‘Hopoungmi’ and ‘Sodammi’ Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) in Cheongju under Climate Change
기후변화에 따른 청주지역에서 고구마(Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) ‘호풍미’ 및 ‘소담미’의 조기삽식 및 수확 시기 재설정
-
Hyeon-Seong Yoo, Eun-Seong Baek, Eun-Bin Hwang, Dong-Geon Nam, Eun-chae Bae, Na-yun Lee, Gun-ho Lee, Sang-Cheol Gwak, Tae-Young Hwang
유현성, 백은성, 황은빈, 남동건, 배은채, 이나윤, 이건호, 곽상철, 황태영
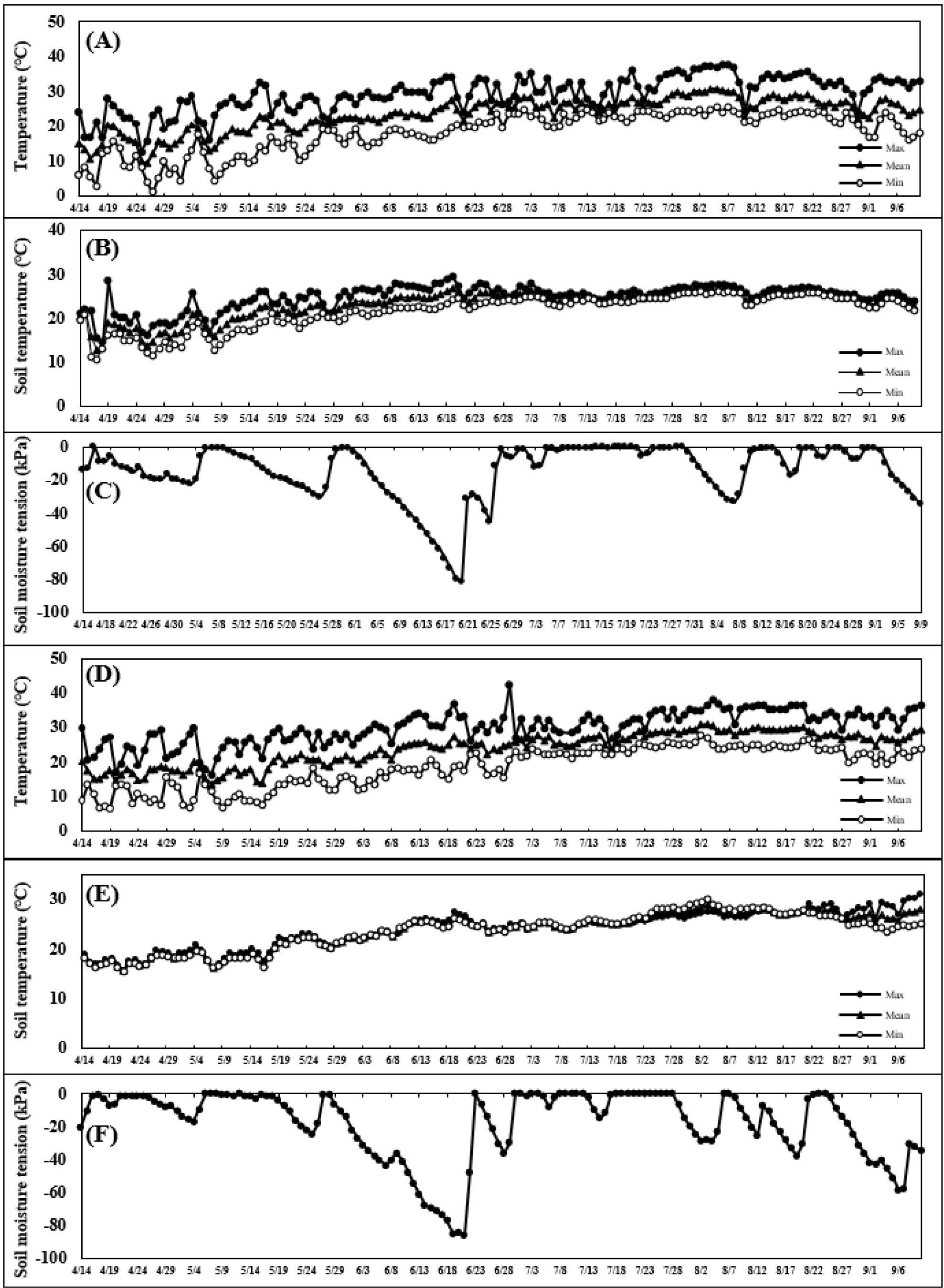
- This study aimed to determine the optimal early transplanting and harvesting periods for sweet potato cultivars, ‘Hopungmi’ and ‘Sodammi’, in response to …
- This study aimed to determine the optimal early transplanting and harvesting periods for sweet potato cultivars, ‘Hopungmi’ and ‘Sodammi’, in response to climate change. Field trials were conducted over two years (2023 and 2024) in Cheongju, South Korea. Transplanting dates were set at five intervals: April 14 (T1), April 19 (T2), April 24 (T3), April 29 (T4), and May 4 (T5), and harvests were conducted at 110 and 120 days after transplanting (DAT). In terms of storage root yields in 2023, ‘Hopungmi’ showed the highest yield at 120 DAT in T4 (2,742.9 kg 10a-1), while ‘Sodammi’ showed the highest yield at 110 DAT in T5 (1,122.3 kg 10a-1). In 2024, the highest yield for ‘Hopungmi’ was observed at 120 DAT in T3 (2,596.0 kg 10a-1), and for ‘Sodammi’, the highest yield was recorded at 120 DAT in T3 (1,819.3 kg 10a-1). The 2024 storage root yields of ‘Hopungmi’ at 110 DAT and ‘Sodammi’ across both cultivation periods were higher than those observed in 2023, which was attributed to the greater cold stress during the early growth stage in 2023 compared with 2024. Correlation analysis between the above shoot growth and storage root yields revealed a significant positive correlation between main vine length and storage root yields. For the soluble solid content of steamed roots, in ‘Hopungmi’, the highest SSC was recorded at T2 for 110 DAT in 2023 (29.1 °Brix) and 2024 (26.8 °Brix). In ‘Sodammi’, the highest SSC was also observed at T2 for 110 DAT in 2023 (27.6 °Brix) and 2024 (27.8 °Brix). These results indicate that the effects of transplanting and harvest schedules vary, depending on annual climatic conditions. Therefore, this study suggests that determining the optimal transplanting and harvest timing for sweet potato under changing climatic conditions can help minimize climate variability and contribute to more stable cultivation. - COLLAPSE
-
Optimizing Early Transplanting and Harvesting Dates for ‘Hopoungmi’ and ‘Sodammi’ Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) in Cheongju under Climate Change
-
Original Research Article

-
Changes of Biomass and Nutrients Production by Type of Sowing of Rye and Hairy Vetch in the Saemangeum Reclaimed Tidal Land
새만금간척지에서 호밀-헤어리베치 파종 방법에 따른 풋거름 수량과 양분 함량의 변화
-
Hyeoun-Suk Cho, Young-Tae Shin, Kwang-Seung Lee, Hak-Sung Lee, Hyeon-Soo Jang, Hee-Kyung Ock, Seo-Young Jeong, Bang-Hun Kang
조현숙, 신영태, 이광승, 이학성, 장현수, 옥희경, 정서영, 강방훈
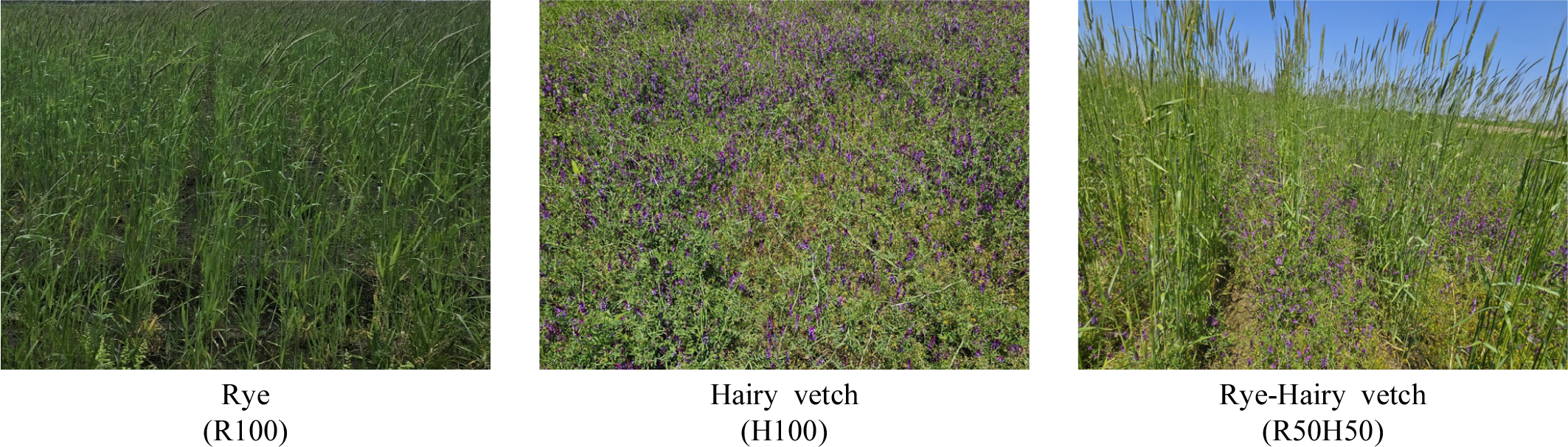
- This study was conducted to evaluate the biomass yield and nutrient production of green manure crops for stable crop cultivation in the …
- This study was conducted to evaluate the biomass yield and nutrient production of green manure crops for stable crop cultivation in the newly reclaimed Saemangeum tidal land. Treatments consisted of rye monoculture (R100), hairy vetch monoculture (H100), and a 50:50 mixed sowing of rye and hairy vetch (R50H50). Plant height increased in the mixed sowing, reaching 175 cm for rye and 94 cm for hairy vetch compared with their monocultures. The highest dry matter yield was obtained in R50H50 (502 kg 10 a-1), showing a 113~260% increase over R100 and H100. Nutrient concentrations in plant tissues ranged from 0.93~2.34% for N, 0.72~1.03% for P2O5, and 1.24~3.84% for K2O, corresponding to nutrient returns of 4.1–6.0 kg N, 1.6~5.2 kg P2O5, and 5.5~12.1 kg K2O per 10a. These results indicate that mixed sowing of rye and hairy vetch is more effective than monoculture for improving soil organic matter and nutrient supply in the Saemangeum reclaimed land. - COLLAPSE
-
Changes of Biomass and Nutrients Production by Type of Sowing of Rye and Hairy Vetch in the Saemangeum Reclaimed Tidal Land
-
Original Research Article

- Mitigation of Heat Shock in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) by Exogenous Application of Plant Extracts
- Ei Ei, Hyun Hwa Park, Yong In Kuk
- Heat shock has serious effects on the quality and yield of crops-especially cucumber. This study aimed to identify a heat-sensitive test plant …
- Heat shock has serious effects on the quality and yield of crops-especially cucumber. This study aimed to identify a heat-sensitive test plant among cereals and vegetables and evaluate the effective concentrations of guava (Psidium guajava), aloe (Aloe vera), garlic (Allium sativum), and alfalfa (Medicago sativa) extracts in terms of hormetic effects based on morphological responses. The study also aimed to optimize the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of heat tolerance in cucumbers subjected to extract treatment. Cucumber shoot fresh weight (27-41%) and plant height (12-26%) were significantly enhanced, whereas maize, barley, and rice showed minimal changes. Guava and aloe extracts increased the total chlorophyll and carotenoid contents in cucumber plants, thus supporting the restoration of photosynthesis. Guava and garlic extracts also increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes and decreased the levels of hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde, thereby minimizing the oxidative damage to cucumber plants. These results suggest that plant extracts can effectively increase the heat tolerance of cucumbers by improving their water status, protecting their photosynthetic function, and enhancing their antioxidant defenses. This approach offers a sustainable and, eco-friendly solution to improve the resistance of plants to stress and supports cultivation under changing climatic conditions. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Research Article
-
Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Expression Efficiency in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) ‘Cheungsam’ via Direct Organogenesis
대마 ‘청삼’의 직접 기관 발생 기반 아그로박테리움 매개 유전자 발현 효율
-
Sung-eun Lee, Hyoseon Choi, Ji-Su Kim, Beom-Gi Kim, Saet Buyl Lee
이성은, 최효선, 김지수, 김범기, 이샛별
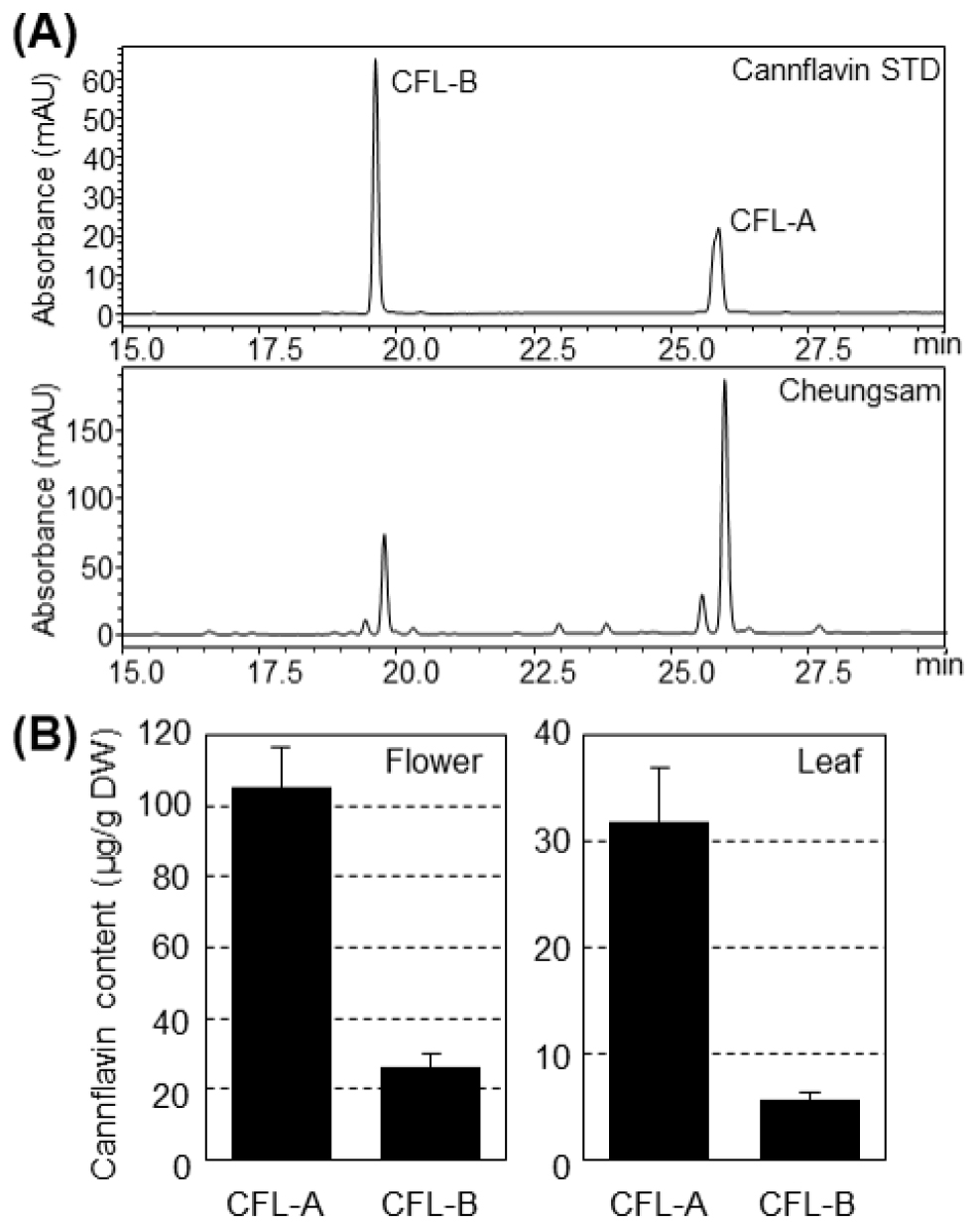
- Cannabis sativa L. is a multipurpose crop valued for its fiber, seed, and medicinal compounds. In addition to cannabinoids, C. sativa produces …
- Cannabis sativa L. is a multipurpose crop valued for its fiber, seed, and medicinal compounds. In addition to cannabinoids, C. sativa produces distinctive prenylated flavonoids known as cannflavins, which exhibit potent anti-inflammatory activity but accumulate at very low levels, limiting their utilization. This study characterized cannflavin traits and developed tissue culture and transformation protocols for the Korean non-drug type hemp cultivar ‘Cheungsam’. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis detected cannflavin A (CFL-A) and CFL-B predominantly in immature female inflorescences, at concentrations of 105.2 µg/g and 26.2 µg/g dry weight, respectively, with lower levels present in leaves. To address regeneration bottlenecks, we optimized a direct organogenesis system using hypocotyl explants of ‘Cheungsam’, which enabled efficient shoot and root formation without callus induction. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation using the RUBY reporter gene achieved transient expression efficiencies of up to 54.2% with strain AGL1. In addition, kanamycin-based selection confirmed the feasibility of producing transgenic lines, although the overall transformation frequency remained modest (6.9%) and betalain accumulation was not uniform or localized as red dots. Collectively, these findings provide the first report of cannflavin profile in ‘Cheungsam’ and establish a regeneration and transformation platform for this hemp cultivar. This work lays the groundwork for future metabolic engineering to enhance cannflavin production and improve the genetic and industrial value of non-drug type hemp in Korea. - COLLAPSE
-
Agrobacterium-mediated Gene Expression Efficiency in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) ‘Cheungsam’ via Direct Organogenesis
-
Original Research Article
-
Evaluation of Nutritional Profiles and Protein Quality of Major Food Crops and Their Cultivars for Protein Supplement Development
단백질 보충소재 적용을 위한 주요 식량작물과 품종별 영양성분 및 단백질 품질 특성
-
Yu-Young Lee, Mihyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kim, Jin-Young Lee, Narae Han, You-Geun Oh, Hye Young Park, Ha Young Park, HaeWon Park, Su-Young Hong
이유영, 김미향, 김현주, 이진영, 한나래, 오유근, 박혜영, 박하영, 박해원, 홍수영
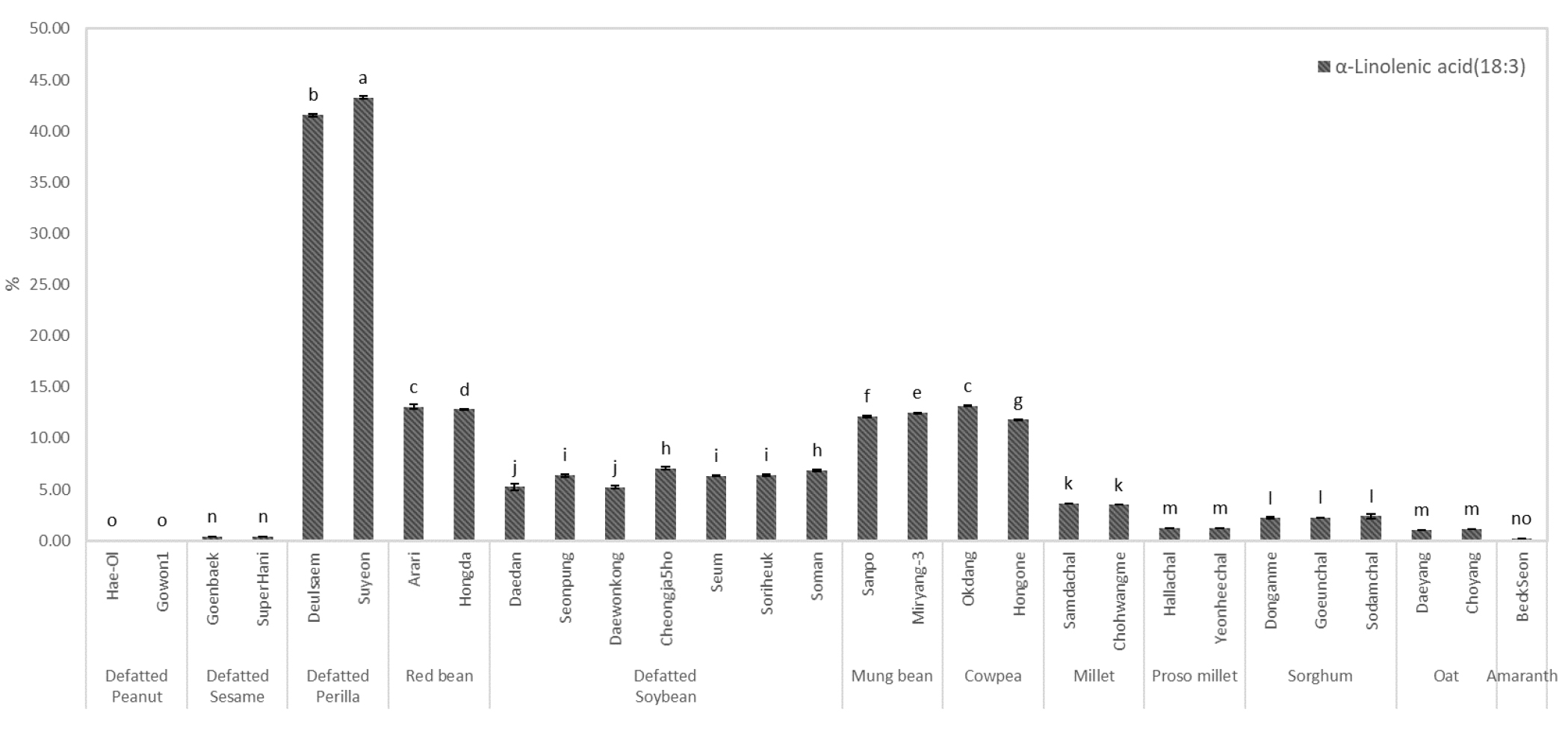
- This study aimed to evaluate the nutritional composition and protein quality characteristics of 28 cultivars from 12 major crops to identify potential …
- This study aimed to evaluate the nutritional composition and protein quality characteristics of 28 cultivars from 12 major crops to identify potential plant-based protein sources for preventing sarcopenia. The proximate composition, fatty acid profile, amino acid composition, and protein qualities such as amino acid score, first limiting amino acid, digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) were analyzed. Crude protein contents were higher in peanut, sesame, perilla, and soybean. Oat and amaranth exhibited relatively higher lipid contents than other crops, while sesame and perilla showed high ash contents. The cereal crops such as foxtail millet, proso millet, and sorghum contained higher carbohydrate levels. Among omega-3 fatty acids known to activate muscle protein synthesis, perilla showed the highest α-linolenic acid content (43.3%), followed by red bean, cowpea, and mung bean, indicating that these crops are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Total and essential amino acid contents were abundant in perilla, soybean, and sesame, and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) such as leucine, isoleucine, and valine, which are directly involved in muscle synthesis, were also high. In the protein quality evaluation, the first limiting amino acids were lysine or cysteine+methionine. PDCAAS values were highest in soybean (‘Daewonkong’ 0.85), perilla (‘Deulsaem’ 0.77), and red bean (‘Arari’ 0.71). These findings suggest that perilla and soybean proteins, rich in BCAAs and α-linolenic acid, possess high protein quality and can be utilized as promising raw materials for developing protein supplements and functional food products. - COLLAPSE
-
Evaluation of Nutritional Profiles and Protein Quality of Major Food Crops and Their Cultivars for Protein Supplement Development
-
Short communication

- Effect of Nitrogen Application to Agronomic Nitrogen Efficiency and Grain Yield in Rice: A Meta-Analysis
- Dain Hong, Sunyoung Lee, Jwakyung Sung
- Nitrogen application is crucial in improving rice productivity; however, its excessive use typically reduces nitrogen-use efficiency and introduces environmental problems. To quantitatively …
- Nitrogen application is crucial in improving rice productivity; however, its excessive use typically reduces nitrogen-use efficiency and introduces environmental problems. To quantitatively evaluate the effects of nitrogen fertilization on agronomic nitrogen efficiency (AE) and grain yield, a meta-analysis was conducted following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. Data from 24 independent studies were analyzed using a random-effects model, and the effect sizes were adjusted using the trim-and-fill method. The mean-effect size of the AE was 3.76 (95% confidence intervals (CI): 2.98–4.54), whereas that of the grain yield was 3.06 (95% CI: 2.41–3.70). Meanwhile, their pooled-effect sizes were 3.42 and 2.33, respectively, with adjustment for publication bias. Subgroup analysis revealed that the AE peaked at 101–150 kg·ha-1, whereas the yield reached its maximum at 251–300 kg·ha-1. These findings suggest that optimizing nitrogen input can enhance both agronomic and environmental efficiencies. This meta-analysis highlights the importance of optimizing nitrogen input to achieve high AE and grain yield in rice production systems. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 The Korean Journal of Crop Science
The Korean Journal of Crop Science
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 The Korean Journal of Crop Science
The Korean Journal of Crop Science











